
After hitting Germany, Taiwan, South Korea, Japan, the US, and the U.K. the Roaming Mantis operation moved to targeting Android and iOS users in France, likely compromising tens of thousands of devices.
Roaming Mantis is believed to be a financially-motivated threat actor that started targeting European users in February.
In a recently observed campaign, the threat actor uses SMS communication to lure users into downloading malware on their Android devices. If the potential victim uses iOS, they are redirected to a phishing page for Apple credentials.
Dropping XLoader
In a report published today, researchers at cybersecurity company SEKOIA say that the Roaming Mantis group is now dropping on Android devices the XLoader (MoqHao) payload, a powerful malware that counts features such as remote access, information stealing, and SMS spamming.
The ongoing Roaming Mantis campaign is targeting French users and starts with an SMS sent to prospective victims, urging them to follow a URL.
The text message informs about a package that has been sent to them and which they need to review and arrange its delivery.
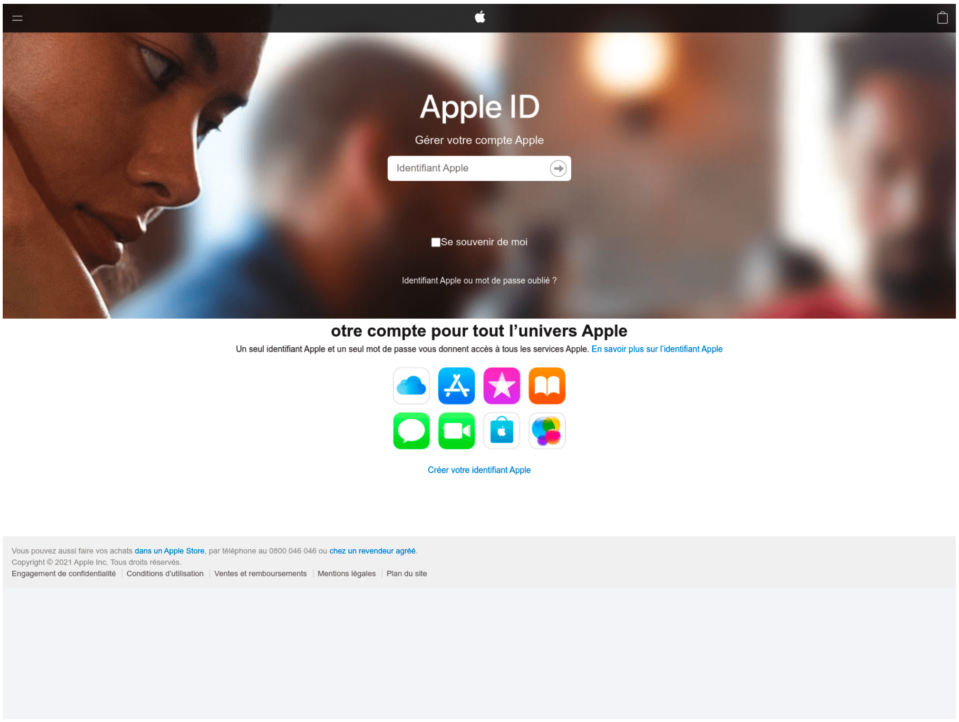
If the user is located in France and are using an iOS device, they are directed to a phishing page that steals Apple credentials. Android users are pointed to a site that delivers the installation file for a mobile app, (an Android Package Kit - APK).
For users outside France Roaming Mantis' servers show a 404 error and the attack stops.
.png)
The APK executes and mimics a Chrome installation, requesting risky permissions such as SMS interception, making phone calls, reading and writing storage, handling system alerts, getting accounts list, and more.
The command and control (C2) configuration is retrieved from hardcoded Imgur profile destinations which are encoded in base64 to evade detection.
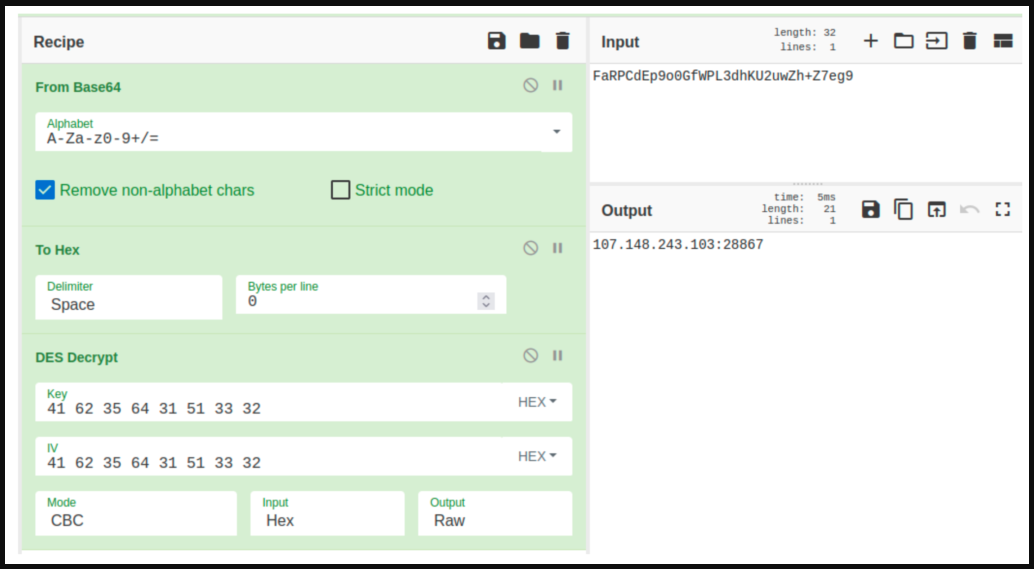
SEKOIA confirmed that over 90,000 unique IP addresses have requested XLoader from the main C2 server so far, so the victim pool might be significant.
The number of iOS users who have handed over their Apple iCloud credentials on the Roaming Mantis phishing page is unknown and could be the same or even higher.
Infrastructure details
SEKOIA’s analysts report that the infrastructure of Roaming Mantis hasn’t changed much since its last analysis from team Cymru last April.
The servers still have open ports at TCP/443, TCP/5985, TCP/10081, and TCP/47001, while the same certificates seen in April are still in use.
“Domains used inside SMS messages are either registered with Godaddy or use dynamic DNS services such as duckdns.org,” explains SEKOIA in the report.
The intrusion set uses over a hundred subdomains, and dozens of FQDN resolve each IP address.
Interestingly, the smishing (SMS phishing) operation relies on separate C2 servers from those used by XLoader, and the analysts could identify nine of those hosted on EHOSTIDC and VELIANET Autonomous Systems.
For a complete list of indicators of compromise for the current Roaming Mantis operation, check out this GitHub page.


Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now